Indoor cellular usage
Gone are the days of referring to a cell phone as a “car phone.” It’s estimated that 80% of cell phone calls originate indoors. Businesses are making the transition to Internet-based communications and increasingly rely on cellular voice and data communications. While mobile devices offer businesses a way to stay in constant contact with team members and customers, many of us stay frustrated with dropped calls and slow data speeds, often inside buildings.
Causes of poor indoor cell signal
Often there is more than just one cause of poor cellular signal. Some of the most common causes include:
Distance to the nearest cell tower
- This cause is a largely rural concern. Very few urban areas suffer from distance concerns anymore.
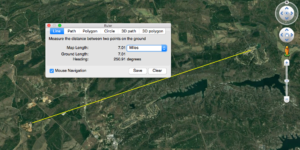
Distance to tower
Terrain
- In Arkansas, this can be a real problem, even in urban areas. Tall hills and deep valleys can cause coverage dead zones. Dense forest can also cause seasonal variation in cellular signal. In urban areas, surrounding buildings can cause RF shadows.
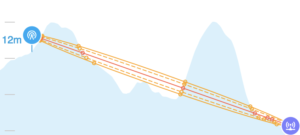
Terrain Obstructions
Building construction
- Stone, brick, block, and concrete attenuate signal. Metal, radiant barrier, and Low-E glass reflect signal. Modern building materials (especially Low-E glass) are often the worst offenders.
- Do you get all of our text messages and voicemail notifications as soon as you walk out to your car? Then you probably have building materials that are efficient at blocking cellular signal, but have adequate signal outdoors.

Low-E glass
Noise/Interference/Carrier Issues
- There might be plenty of signal (quantity) in an area, but not good quality because there may be multiple towers on the same (or nearby) frequency. Think of it this way: It’s easier to tell what one person is saying to you if only one of them is speaking. If multiple people are talking at the same time, the result is just noise instead of any type of communication.
- Sitting on a border with weak signal from two cells may be the worst situation of all.Weak signal and continually switching between towers causes even more instability with voice and data services.
- In high traffic areas, especially along congested roadways, high-density office areas, or near stadiums, signal from the tower can fluctuate as load increases.
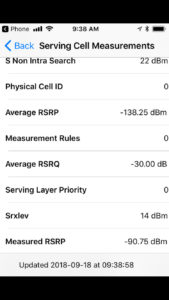
Carrier LTE Info
Improving Poor Cell Signal
Cell signal boosters use existing cell signal (typically outdoors), capture it and amplify it by 32 times or more to improve service where you need it most (typically indoors). 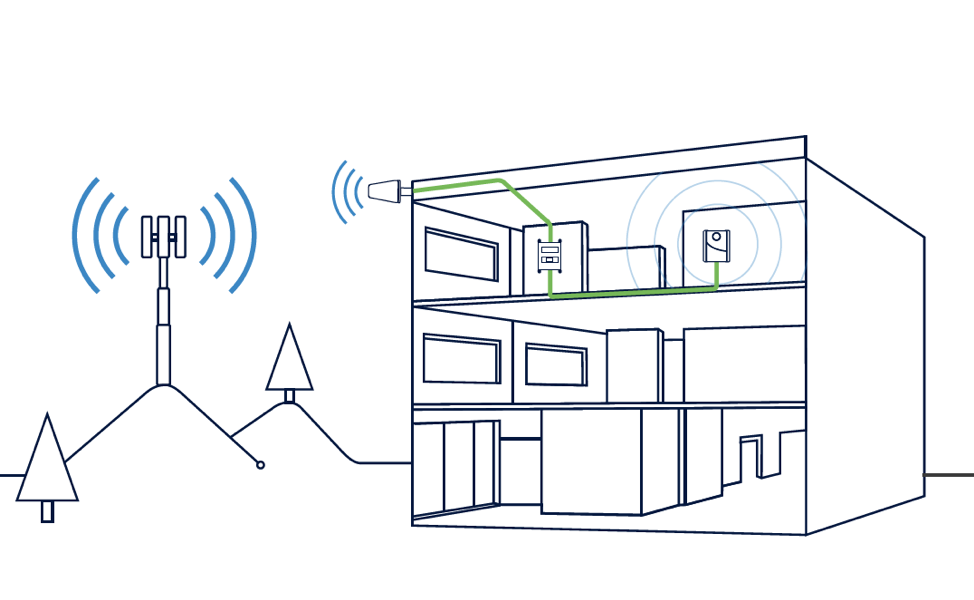
These boosters are passive distributed antenna systems that place antennas and amplifiers in different areas to capture strong signal and make it accessible where you need it. These systems can be installed quickly and cost effectively.
If you’d like to learn more about how a cell signal booster can help you improve signal and eliminate the frustration of dropped calls and slow data speeds, contact us at C2 Networks today using the form below.

